-
A Lithium Amide-Borohydride Solid-State Electrolyte with Lithium-Ion Conductivities Comparable to Liquid Electrolytes
Y. Yan, R.-S. Kühnel, A. Remhof, L. Duchêne, E.C. Reyes, D. Rentsch, Z. Lodziana and C. Battaglia
Advanced Energy Materials, (2017), p1700294


DOI:10.1002/aenm.201700294 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF | Supporting Info
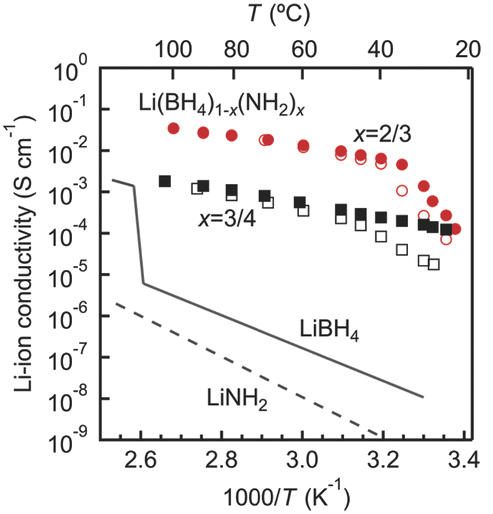
High ionic conductivity of up to 6.4 ×10−3S cm−1 near room temperature (40 °C) in lithium amide-borohydrides is reported, comparable to values of liquid organic electrolytes commonly employed in lithium-ion batteries. Density functional theory is applied coupled with X-ray diffraction, calorimetry, and nuclear magnetic resonance experiments to shed light on the conduction mechanism. A Li4Ti5O12 half-cell battery incorporating the lithium amide-borohydride electrolyte exhibits good rate performance up to 3.5 mA cm−2 (5 C) and stable cycling over 400 cycles at 1 C at 40 °C, indicating high bulk and interfacial stability. The results demonstrate the potential of lithium amide-borohydrides as solid-state electrolytes for high-power lithium-ion batteries.